Working Principle of Hydrocyclone
Introduction
Hydrocyclone separation technology is an efficient and energy-saving separation method, with the hydrocyclone serving as its key component. Oily wastewater is injected tangentially into the hydrocyclone at a certain pressure or velocity, causing it to rotate rapidly inside the device and generate a centrifugal force field. Under the action of centrifugal force, the water, which has higher density than the oil, is thrown outward toward the wall and moves downward to be discharged as the underflow. Meanwhile, the less dense oil migrates to the center and moves upward, eventually being discharged as the overflow, thereby achieving liquid separation.
Principle
The hydrocyclone oil separator consists of multiple conical tubes. Both ends of the conical tubes are fixed by two partition plates inside a cylindrical container, which is divided into three sections: the inlet chamber, the outlet chamber, and the oil collection chamber. The working principle of the conical hydrocyclone tubes is as follows: oily wastewater enters the inlet chamber through the tangential inlet at the end of the conical tube and flows in a high-speed spiral motion along the inner wall of the conical tube toward the increasingly narrower outlet end (the tail). The high-speed rotation generates centrifugal force, which increases as the rotational motion accelerates.
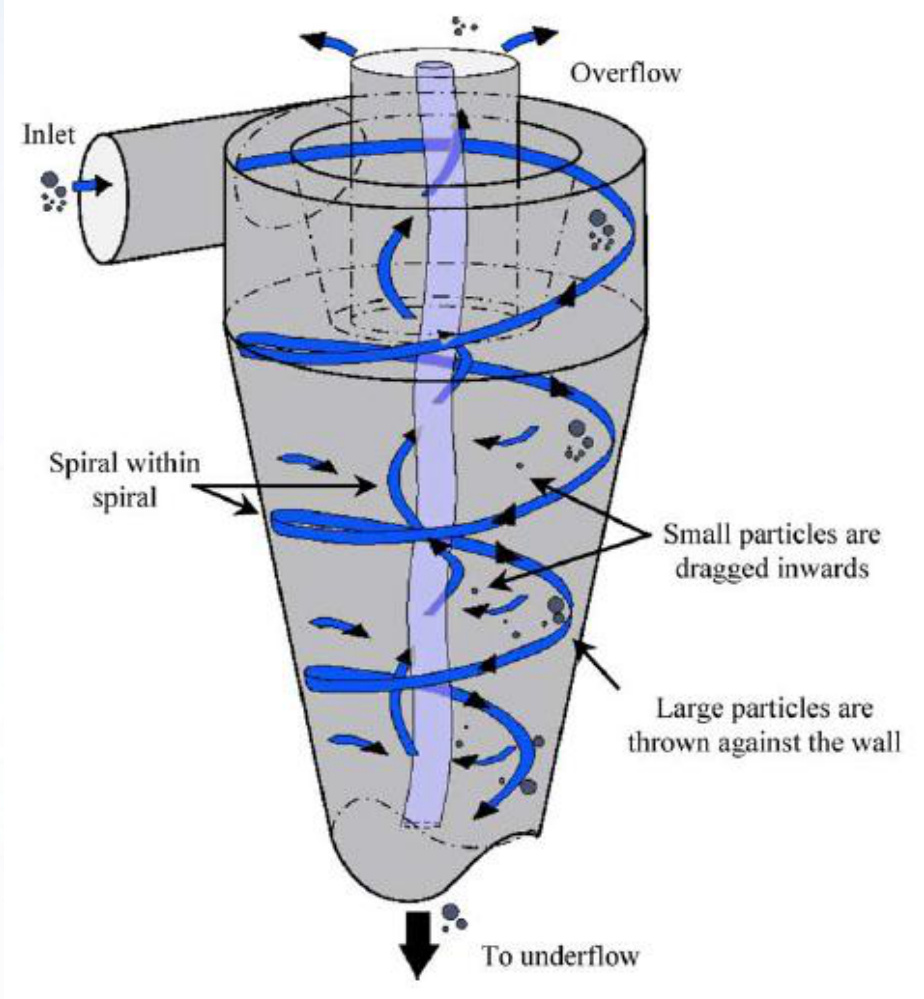
Schematic Diagram
Due to the density difference between oil and water in oily wastewater, the less dense oil droplets are pushed toward the center by the centripetal force—the reaction force to centrifugal force. The centrifugal force increases from the inlet to the outlet, meaning the centripetal force acting on the oil droplets also increases accordingly. As a result, the oil droplets at the center are pushed from the outlet end (the narrower end) toward the inlet end (the wider end). Eventually, the oil is extruded through the oil guide pipe at the top of the outlet end into the oil collection chamber, thereby separating the oil droplets from the water. The water, on the other hand, enters the outlet chamber through the narrower end.
Application
A density difference of generally more than 0.05 between oil and water is required. For non-emulsified oily wastewater, the use of hydrocyclones can achieve high oil removal efficiency. However, for emulsified oily wastewater, demulsification treatment should be carried out prior to hydrocyclone separation. The diameter of oil droplets separated by hydrocyclones is typically above 15 ㎛.
Hydrocyclone oil separators are widely applicable in crude oil dehydration and oily wastewater treatment. They can also be used in chemical, mechanical, oil refining, oil port, ship, offshore platform, and environmental protection industries for treating oily wastewater and separating liquid-liquid mixtures with density differences. For high-concentration applications, a two-stage series configuration can be employed.
