AI-Powered Water: How Smart Technologies Are Revolutionizing Power Plant Wastewater Treatment
The Transformation from Traditional to Smart: Breaking the Pain Points of Power Plant Wastewater Treatment
In traditional perception, power plant wastewater treatment systems are often associated with keywords such as "bulky equipment", "complex pipelines", and "manual inspection records". However, with the penetration of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and big data analytics, this traditional industrial scenario is undergoing a subversive transformation — the era of "smart water management" has officially begun. These cutting-edge technologies are like equipping the wastewater treatment system with a "smart brain" and "acute senses", enabling real-time control of the entire treatment process, as well as proactive optimization and risk prediction. This article will take you into this integrated scenario to reveal how AI and big data empower power plant wastewater treatment.
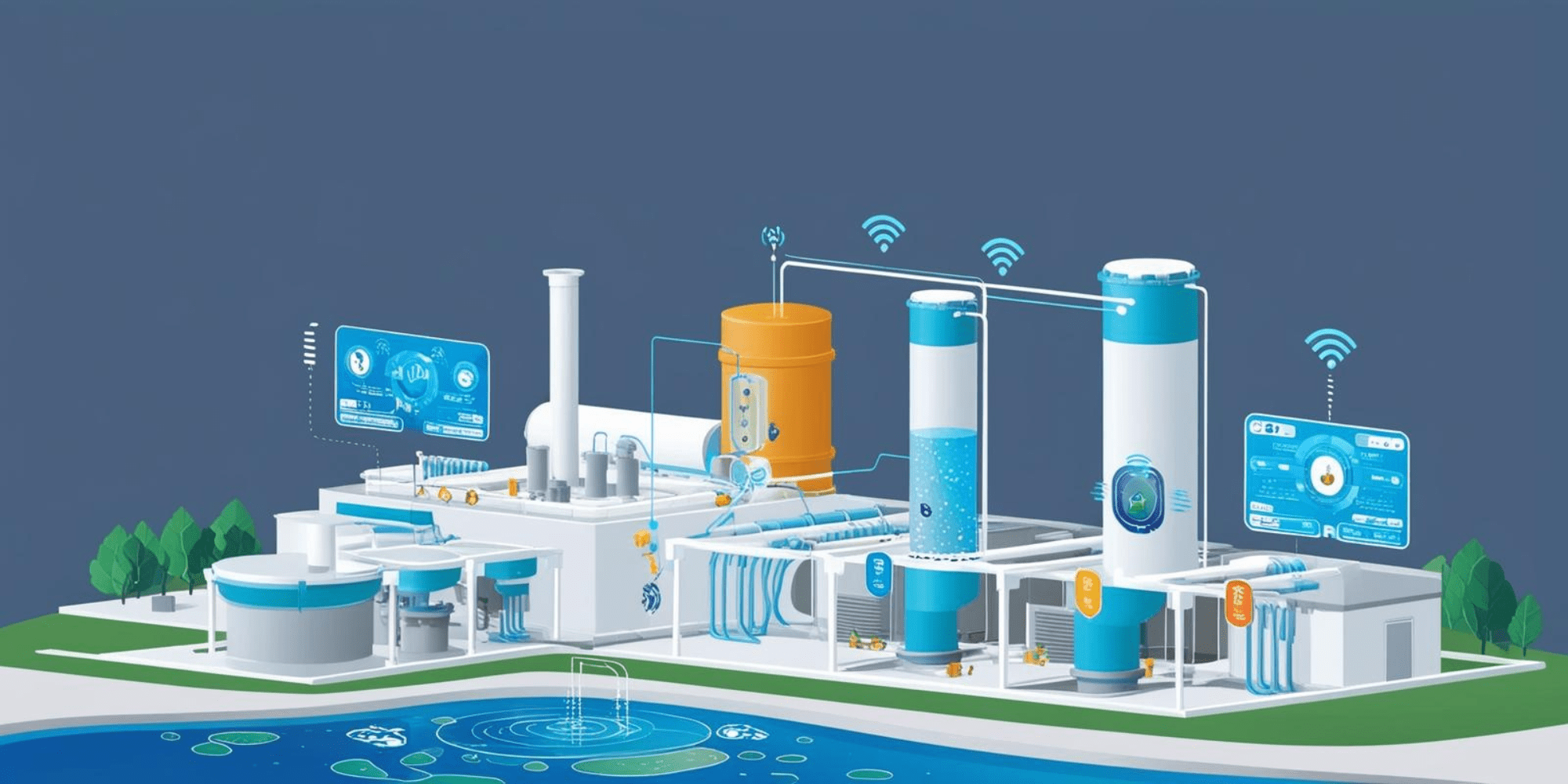

To understand the core value of "smart water management", we first need to clarify the pain points of traditional power plant wastewater treatment. Power plant wastewater has complex components; coal-fired power plants alone produce various types such as flue gas desulfurization (FGD) wastewater, circulating cooling water blowdown, and chemical water treatment wastewater. Different types of wastewater have vastly different treatment processes and parameter requirements. Under the traditional treatment mode, relying on manual monitoring of water quality indicators and adjustment of operating parameters not only results in delayed responses but also easily leads to fluctuations in treatment efficiency due to human errors. At the same time, equipment failures are often only detected after they occur, which may cause risks such as system shutdown and substandard wastewater discharge. In addition, the control of energy consumption and chemical dosage relies entirely on experience, making it difficult to achieve precise optimization and resulting in resource waste. The combination of AI, IoT, and big data can precisely address these issues.
IoT: The "Sensory Nerves" of Smart Water Management
The Internet of Things (IoT) serves as the "sensory nerves" of smart water management, responsible for connecting the "last mile" of data collection. In power plant wastewater treatment systems, a large number of intelligent devices equipped with sensors are deployed at key nodes such as sedimentation tanks, filter tanks, membrane modules, and chemical dosing units, real-time collecting massive amounts of data including pH value, dissolved oxygen, suspended solids concentration, salinity, flow rate, pressure, and equipment operating temperature. These sensors are like small tentacles spread across the system, converting previously scattered and imperceptible operating states into quantifiable and transmissible data signals, which are transmitted to the big data platform via 5G or industrial Ethernet, providing basic support for subsequent intelligent analysis. For example, in the neutralization process of FGD wastewater treatment, sensors can collect pH data once per second — a qualitative leap in accuracy and real-time performance compared to traditional manual testing once per hour.
Big Data Analytics: The Data Hub of Smart Water Management
Big data analytics is the data hub of smart water management, responsible for filtering, integrating, and mining massive amounts of data. A power plant wastewater treatment system can generate tens of thousands or even hundreds of thousands of data points per day. While these data may seem scattered, they actually contain the laws of system operation. Through the construction of standardized data models, the big data platform integrates and analyzes collected water quality data, equipment operation data, energy consumption data, and chemical dosage data to sort out the correlation between parameters. For example, by analyzing chemical dosage and effluent quality data under different influent concentrations, the optimal chemical dosage ratio can be accurately identified; by comparing energy consumption data under different seasons and loads, the operating range with the lowest energy consumption can be found. At the same time, the platform can integrate historical and real-time data to form a full-process data traceability chain. Once problems such as substandard water quality occur, the source can be quickly traced back, providing a basis for troubleshooting.
AI: The "Core Brain" Driving Proactive Management
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the "core brain" of smart water management, enabling the upgrade from "passive response" to "proactive prediction". Based on the massive data provided by the big data platform, AI algorithms acquire core capabilities such as parameter optimization, fault prediction, and intelligent decision-making through continuous learning and training. In terms of parameter optimization, the AI system can automatically adjust key parameters such as chemical dosage, stirring speed, and membrane module operating pressure according to real-time water quality data and influent flow changes, ensuring stable and up-to-standard effluent quality while minimizing chemical and energy consumption. For example, a coal-fired power plant reduced chemical consumption by more than 15% and saved hundreds of thousands of yuan annually by optimizing the chemical dosing process of FGD wastewater treatment through AI.
