Revolutionizing Water Reuse: The Critical Role of Wastewater Treatment
Introduction: The Importance of Wastewater Treatment
Wastewater treatment technologies are crucial for balancing environmental health and public safety. Proper treatment of wastewater helps prevent contamination of natural water sources and the spread of diseases. As urban populations grow and industrial activities expand, understanding and applying effective wastewater treatment methods is increasingly vital to safeguard water resources.
Defining Wastewater and Treatment Stages
Wastewater encompasses water that has been used and contaminated, including domestic sewage, industrial runoff, and stormwater. The goal of wastewater treatment is to eliminate these pollutants, rendering the water safe for release into the environment or for reuse.
The treatment process typically consists of three stages: primary, secondary, and tertiary. Primary treatment involves the removal of large particles and suspended solids through physical processes like screening and sedimentation. Secondary treatment uses biological methods to degrade organic materials and nutrients, often employing systems such as activated sludge or trickling filters. Finally, tertiary treatment aims to remove the remaining contaminants, including pathogens and trace chemicals, using advanced techniques like filtration, disinfection, and membrane filtration.
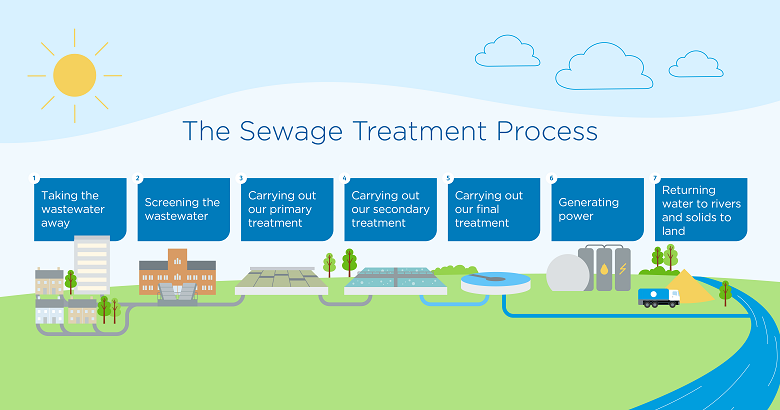
The Primary Treatment Process
During the primary treatment stage, the focus is on removing larger solids and debris. Screening, the initial step, filters out large objects, while sedimentation allows denser particles to settle at the bottom of the treatment tank. This process is essential for lowering the organic load and preventing clogging during subsequent stages.
Secondary Treatment: Biological Filtration
Secondary treatment targets the biological degradation of organic contaminants in wastewater. The activated sludge method uses microorganisms to break down pollutants, while trickling filters depend on the growth of microorganisms on a surface to remove organic material. These methods effectively reduce the biological oxygen demand (BOD) and remove harmful substances from the water.
Tertiary Treatment: Final Purification
Tertiary treatment is the final phase in wastewater treatment. This stage employs advanced processes like filtration (e.g., sand or activated carbon filters) to capture smaller particles. Disinfection methods such as chlorination or ultraviolet (UV) light are then used to kill pathogens. For the highest quality water, membrane filtration techniques such as reverse osmosis can be applied, ensuring the water is safe for reuse or discharge.
Innovations in Wastewater Treatment Technologies
Wastewater treatment is a rapidly advancing field, with ongoing research into innovative technologies aimed at improving efficiency and sustainability. Membrane bioreactors (MBRs) combine biological treatment with membrane filtration, offering a compact and energy-efficient solution. Additionally, advanced oxidation processes (AOPs), including ozonation and UV/hydrogen peroxide treatment, have shown promise in breaking down persistent organic pollutants. However, these emerging technologies may come with challenges such as high costs, increased energy requirements, and maintenance concerns.
Real-World Examples of Effective Treatment Systems
Several cities and regions have successfully implemented advanced wastewater treatment systems. For example, the East Bay Municipal Utility District in California utilizes tertiary treatment to produce high-quality recycled water for industrial and agricultural uses. This system reduces dependency on freshwater sources while promoting sustainability. In Singapore, a densely populated urban area, membrane bioreactors have been incorporated into wastewater treatment plants to meet the city's increasing water demands.
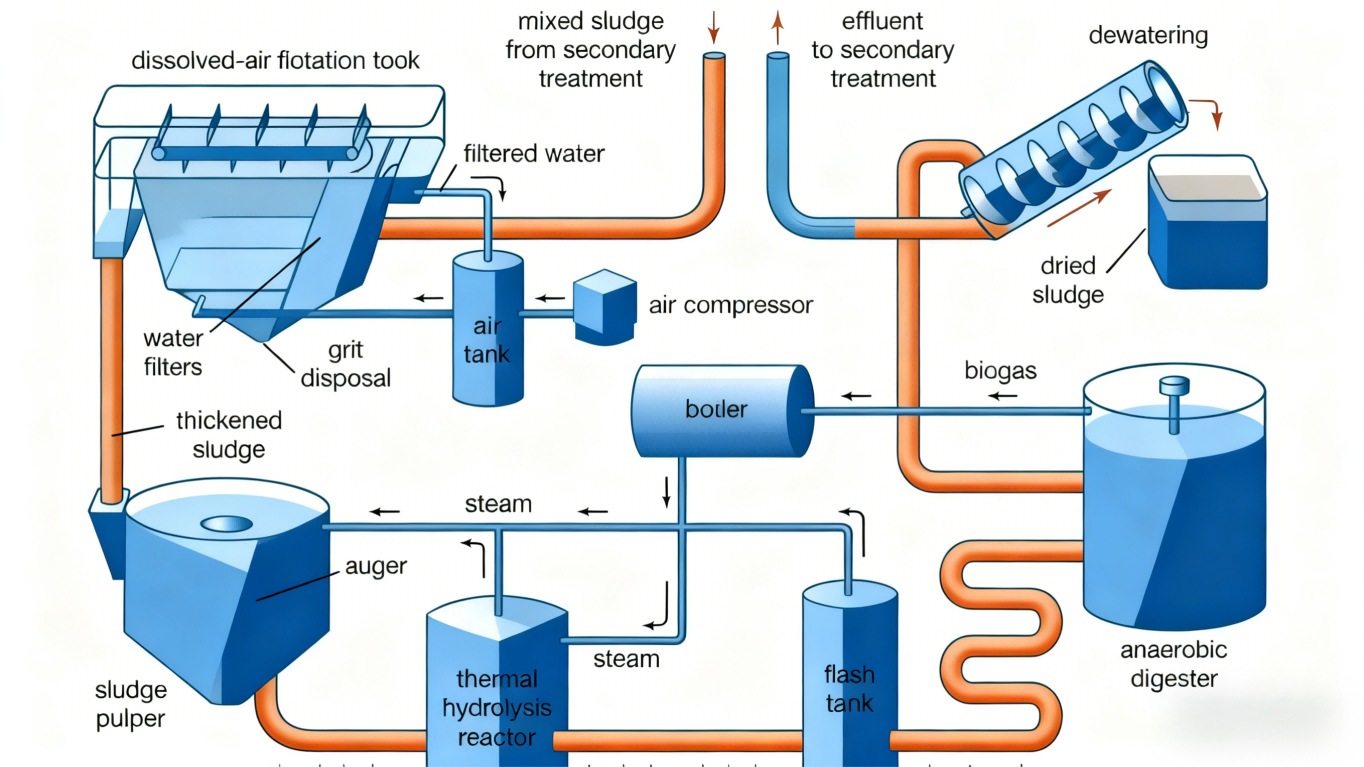
Current Trends Shaping Wastewater Treatment
Recent advancements in wastewater treatment focus on increasing energy efficiency, recovering valuable resources, and adopting decentralized systems. Anaerobic digestion, which captures the energy in wastewater’s organic matter to generate biogas, is one such energy-efficient process. Resource recovery techniques, like extracting nitrogen and phosphorus from wastewater, aim to repurpose these nutrients for agricultural or industrial applications. Decentralized treatment systems, such as modular treatment units or constructed wetlands, provide localized solutions that can lower infrastructure costs and reduce energy consumption.
Overcoming Challenges in Wastewater Management
Despite the clear advantages of wastewater treatment technologies, challenges remain. The high initial costs can be prohibitive for lower-income regions or developing countries. Public acceptance of recycled wastewater, especially for potable use, can also be a barrier in some areas. Additionally, adhering to regulatory standards, which are constantly evolving, requires significant resources from wastewater treatment facilities.
Conclusion: A Sustainable Future for Wastewater Treatment
Wastewater treatment is a cornerstone of both environmental sustainability and public health protection. By removing contaminants, these technologies ensure that water bodies remain clean and that water resources can be reused safely. The wastewater treatment field continues to evolve, with innovative technologies providing solutions to global water challenges. By overcoming existing barriers and embracing the latest trends, we can achieve a more sustainable and resilient approach to wastewater management.
