Reverse Osmosis Membrane Separation Technology: Advantages, Challenges and Solutions
1. Advantages and Wide Applications of Reverse Osmosis Membrane Separation Technology
As an advanced liquid purification method, reverse osmosis (RO) membrane separation technology offers a host of advantages over conventional treatment processes, such as remarkable cost-effectiveness, convenient operation and maintenance, no need for acid-alkali addition, and a small footprint. For these reasons, it has been widely applied in various fields including seawater and brackish water desalination, high-purity water production, as well as the concentration and recovery of chemical materials.

With the continuous expansion of membrane product categories, gradual improvement of membrane performance, and ongoing optimization of RO systems, the application scope of this technology is also growing steadily in municipal wastewater reuse and industrial wastewater purification.
2. Working Principle and Challenges of Reverse Osmosis Process
The reverse osmosis process relies on a certain level of pressure (typically ranging from 1 to 10 MPa) to drive water molecules in the solution to penetrate specific separation membranes, thereby achieving the separation, extraction, purification and concentration of substances. This technology can not only effectively remove various types of salts and ionic substances, but also exhibits excellent retention capacity for organic compounds, colloids, bacteria and viruses.
In actual operation, the reverse osmosis membrane can convert approximately 80%–85% of the feed water into clean permeate. All the retained substances accumulate in the concentrate, which accounts for 15%–20% of the feed water volume, and the pollutant concentration in the concentrate is usually 2 to 3 times that of the feed water. Failure to properly dispose of this high-salinity, high-organic-concentration concentrate will not only result in the massive waste of valuable water resources, but also potentially trigger severe environmental pollution issues.
3. Water Quality Characteristics of Reverse Osmosis Concentrate
The water quality characteristics of reverse osmosis concentrate depend primarily on the source of the feed water. Concentrate generated from wastewater treatment systems generally has significantly higher electrical conductivity, total dissolved solids (TDS) and hydrogen ion content compared with that produced by seawater desalination processes.
Such concentrate is mainly composed of soluble inorganic salts and refractory small-molecule organic compounds. The organic components may include non-degradable chemical substances from domestic sewage (e.g., pesticides, personal care products, pharmaceutical residues, endocrine-disrupting compounds), residues generated during water treatment processes (such as soluble microbial products, partially biodegradable organic matter, and scale inhibitors), as well as various biological substances (including bacteria, viruses, oocysts and cell debris), all of which pose potential threats to the ecological environment. The inorganic salts are mainly composed of anions such as chloride, carbonate, bicarbonate, sulfate and nitrate, along with cations like calcium, magnesium and sodium.
4. Sinokle's Innovative Solution for RO Concentrate Treatment
To address the characteristics of reverse osmosis concentrate, such as large treatment volume and high salinity, and based on the concept of zero liquid discharge (ZLD) and resource recovery, Sinokle Technology has launched an innovative treatment solution—high-efficiency catalytic ozonation technology—specifically designed to tackle the challenges of RO concentrate treatment.
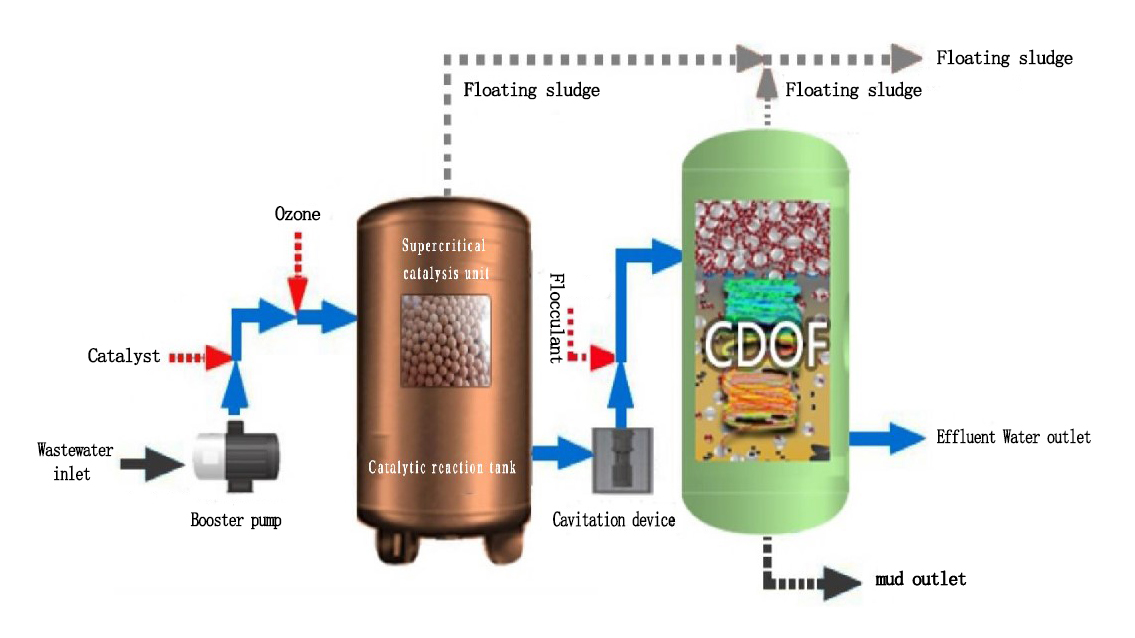
The process illustrated in the figure is CDOF (Cyclonic Dissolved Ozone Flotation unit), an independently developed technology by Sinokle. CDOF innovatively integrates advanced ozonation technology, cyclonic separation technology and dissolved air flotation technology, realizing the efficient and comprehensive removal of various refractory wastewater contaminants.
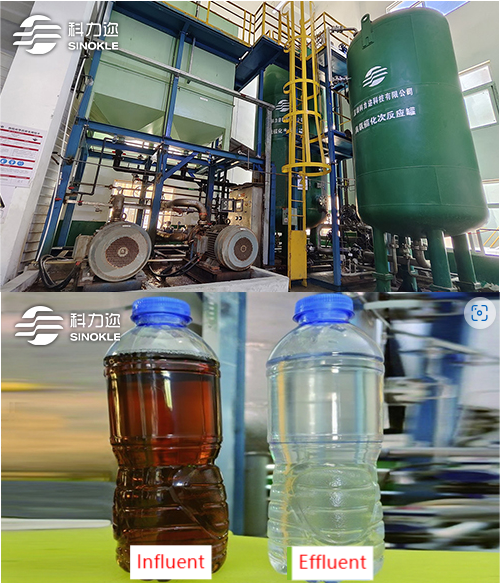

The catalytic ozonation process features a short flow path, simple equipment, small and compact treatment units, and a small footprint. It requires few electrical equipment, resulting in low power consumption, reduced operating costs, easy operation and automatic control, which simplifies the requirements for on-site operation. When the water volume and quality fluctuate, it allows for adjustment of water quantity and quality, demonstrating strong adaptability and shock load resistance. Moreover, it can be combined with other technologies (such as biochemical processes) to give full play to the respective advantages of each process, further enhancing the overall treatment efficiency.
